Factor Tree
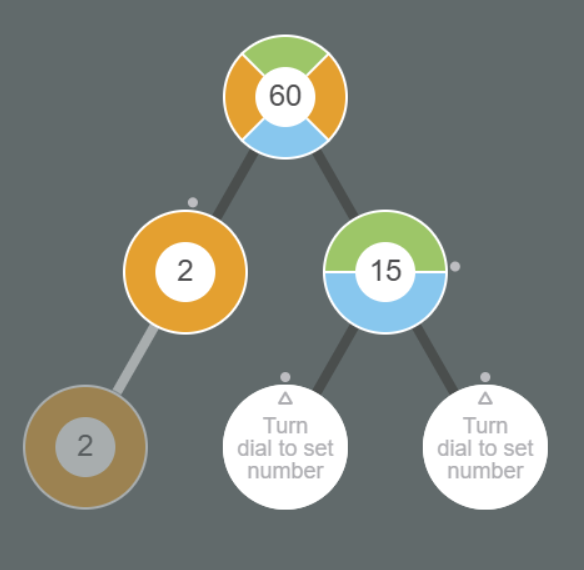
The Factor Tree interactive uses number circles in a binary tree configuration to build factor trees. The number at the root of the tree is specified in the URL. The factors below the root number are set using the small dot outside the perimeter of the circle as a dial. When a combination of two factors correctly multiply to the number above them, the connections thicken and turn white. When, a level of the tree correctly multiplies to the root number the multiplication statement is shown. After the factor tree is completed and results in prime numbers at all the leaf nodes of the tree, the words "Prime Factored Form" appear below the tree.
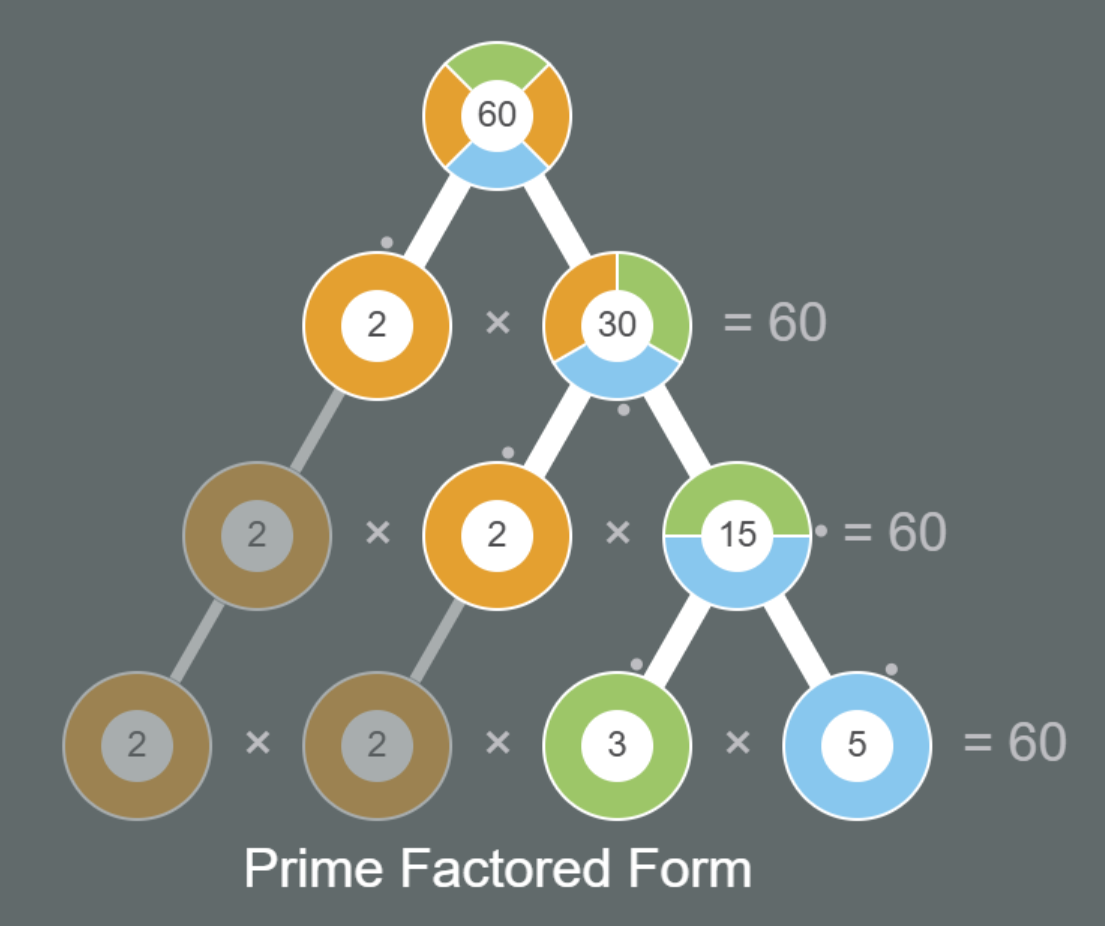
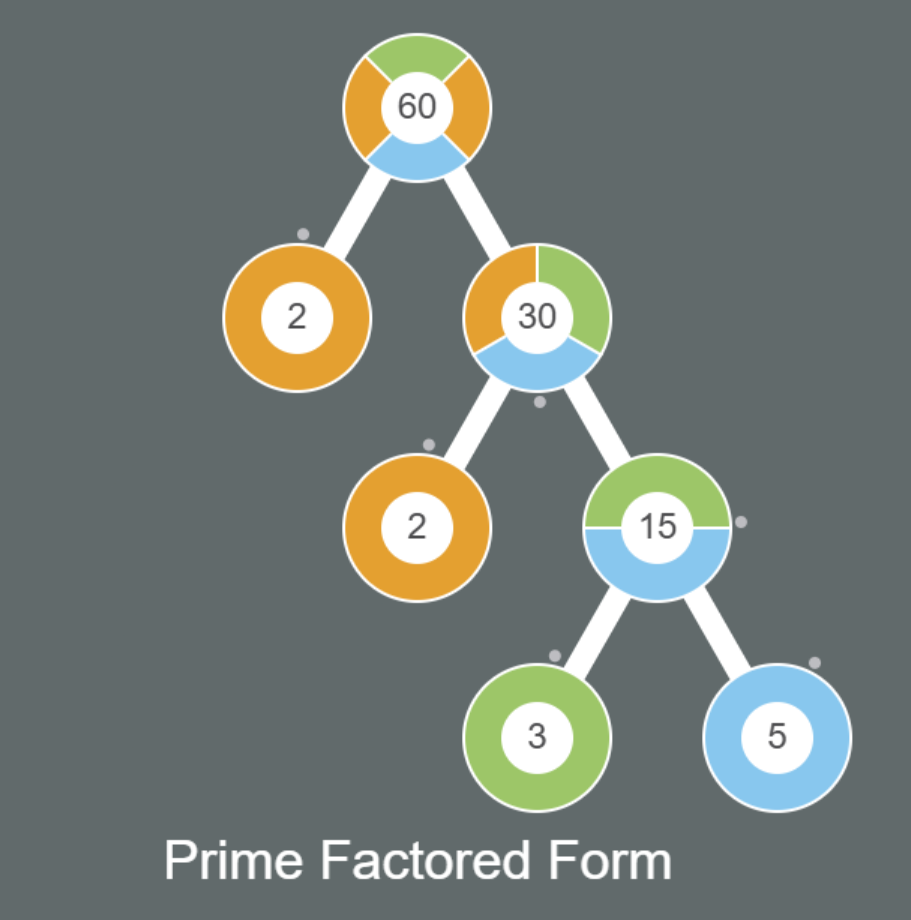
The interactive can be configured to show the factor tree in Layered Equality format, where primes are carried down to lower layers to complete the multiplication statement on each layer. Or, the interactive can be configured to display the tree in Pruned to Prime format, where a branch of the tree ends at the first level where a prime factor is found.
Various other configuration options are available. The dials, "Prime Factored Form" text, and multiplication statement feedback may be turned on or off. The tree may also be prepopulated with values below the root number. Try the examples below and review the documentation for more insights.
The examples below demonstrate different capabilities of the interactive. Some of those capabilites are configured using search parameters in the URL. Note the search parameters in the examples and click over to the Documentation tab for a complete explaination of the configuration options with URL examples.


Max Limiter
Constrain the maximum value to half the parent value to improve control for large numbers.
Try it!Basic Usage
The required parameter in the URL is the trees=X, where X equals the number at the root of the tree. The Layered Equality factor tree duplicates primes on decending levels to maintain a product on each level that equals the number at the root of the tree. Those duplicated primes are slightly dimmer than the other factors to give emphasis to the pruned version of the tree. In the interactive code, these duplicated primes are called shadows, and they can be turned on or off using a search parameter in the URI. For example, the URI for the Pruned to Prime Factors calls the same web page as Layered Equality, but it adds the search parameter shadows=false to turn off the duplicated primes.
Examples of the URIs:- factor-tree-grid.html?trees=24 (Layered Equality)
- factor-tree-grid.html?trees=24&shadows=false (Pruned to Prime)
Parial or Fully Populated Trees
The search parameter to initialize the tree is called trees and it follows a format where levels are separated by '_' characters and factors on each level are separated by the '.' character. It is possible to populate the factors on lower levels of the tree by separating levels using the '_' sharacter and factors using the '.' character. For example, a factor tree for 45 could be fully populated using the parameter trees=45_5.9_3.3. The factors 5 and 9 appear below the 45, and the factors 3 and 3 appear below the 9.
It is not necessary to set the value for shadows, only pairs of factors that you want to appear at each level. The interactive automatically associates pairs of children with parents in the level above from left to right. If you want to populate blank factors for the user to set to the left of other children with explicit values, just pad the blank factors with the number 0. One can see how different factor trees can be constructed as a starting point for further exploration.
Example URIs:- factor-tree-grid.html?trees=24 (Start with 24)
- factor-tree-grid.html?trees=24_8.3 (Start with 24 and 8 x 3)
- factor-tree-grid.html?trees=24_0.3 (Start with 24 and ? x 3)
- factor-tree-grid.html?trees=24_6.4_2.3 (Start with 24 and 6 x 4 and 2 x 3 x ? x ?)
- factor-tree-grid.html?trees=24_6.4_0.0.2.2 (Start with 24 and 6 x 4 and ? x ? x 2 x 2)
- factor-tree-grid.html?trees=24_6.4_3.2.2.2 (Prime factored form)
- factor-tree-grid.html?trees=24_8.3_2.4_2.2 (Prime factored form)
- factor-tree-grid.html?shadows=false&trees=24_8.3_2.4_2.2 (Prime factored form, no shadows)
- factor-tree-grid.html?trees=24_10.3_2.4_2.2 (Mistake in the middle)
Display Options
We have seen, above, that using the display option shadows=false results in a Pruned to Prime factor tree.
However, if you want to use this interactive to generate factor tree images, and want to reduce the clutter in the image or the
ability for the user to edit the tree, there are also parameters for disabling the dials, row products, and prime factored
form feedback. The parameters are: dials=false, products=false, and pff=false
- factor-tree-grid.html?trees=24_2.12_2.6_2.3&dials=false&products=false&pff=false (Complete tree with no dials, products, or prime factored form feedback)
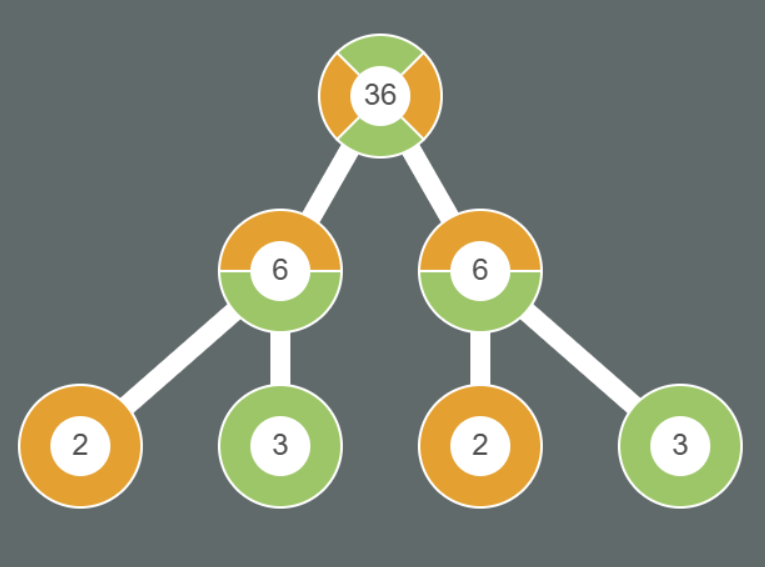
Grids of Trees
Sometimes, it is advantageous to display more than one factor tree in the same window. This presentation can promote noticing differences between trees, based on their root value. Therefore, the factor tree interactive has the capability to display different factor trees in a 2 x n grid. The display parameters are inherited by all the factor trees displayed in the grid, but the values in the trees can be unique.
Multiple trees may be initialized through the trees parameter, by separating them with the '~' character.
Example URIs:- factor-tree-grid.html?trees=6~10~14~21 (Compare numbers with two prime factors)
- factor-tree-grid.html?trees=84_4.21~84_7.12~84_6.14~84_2.42 (Compare different factoring options for 84)
By default, the grid of trees has two columns. However, it may be preferable to have a different number of columns. Use the columns parameter to specify the number of columns in the grid.
Example URIs:- factor-tree-grid.html?trees=6~10~14&columns=1 (Vertical array)
- factor-tree-grid.html?trees=6~10~14&columns=3 (Horizontal array)
Optimizing Control
With larger numbers, the dial on the number circle could be subdivided into very small sections. This can make dialing in a specific number difficult, particularly with track pads. One way to make the dial easier to control is to move the mouse away from the center of the number circle. This creates more circumferential distance per number around the circle. However, this method may not be obvious to all users. Therefore, a max limiting algorithm was added to the factor tree interactive which limits the maximum number of each circle to one half of the parent number. To guarantee that dial does not become too quantized, a minimum limit for the maximum value is set to 10. For example, a child circle under the number 90 is limited to a maximum value of 45. However, a circle presented under the number 4 would still have a maximum value of 10. Enable the maximum limit algorithm by setting the search parameter mla=true
Example URIs:- factor-tree-grid.html?trees=90&mla=true (Limit max values)
- factor-tree-grid.html?trees=4&mla=true (Max forced to 10)